Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver. It is more common in alcoholics. However, the incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease has also increased in the last few decades. The main reason for this is not getting used to proper diet and unhealthy lifestyle. People who are overweight, have diabetes or pre-diabetes, are at higher risk of developing this disease. Dhaka Medical College and Hospital Liver Department associate professor and department head Dr. wrote in detail. Farooq Ahmed
In the human body, the liver is an essential gland located on the upper right side of the abdomen below the rib cage. The liver performs many functions necessary for our body. Among these, it is important to purify the toxic substances of the blood, make and secrete bile, which helps in the digestion and absorption of fat or fatty foods from the esophagus, making meat, maintaining the immune system of the body, keeping the blood density and clotting process intact, etc.
About five percent of liver cells are fat, which is normal, and when excess fat accumulates for any reason, it is called fatty liver disease. There are two types of fatty liver, Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) which is caused by long-term heavy drinking and if proper measures (especially abstinence from alcohol) are not taken, it can lead to long-term liver disease i.e. Liver Cirrhosis. Another is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) which is commonly associated with diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, excess fat in the blood etc. These diseases are collectively called metabolic syndrome. Even in the absence of metabolic syndrome, obesity alone may predispose someone to fatty liver. BMI or Body Mass Index is used to measure obesity.
Taking a person’s weight in kg and height in meters, Body mass index or BMI is obtained by dividing the weight by the square of the height. A BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight, 18.5-24.9 is normal weight, 25-29.9 is overweight and a BMI greater than 30 is considered obese or overweight. Dependence on technology, lack of physical activity and consumption of extra caloric food than required are considered as causes of obesity. Obesity and NAFLD have increased significantly over the past decades. Although fatty liver is more common in obese people, sometimes thin people also suffer from fatty liver. Fatty liver disease can occur in certain types of drugs, alcohol, hormonal factors and hereditary factors.
A BMI of 9 is overweight and a BMI of over 30 is considered overweight or obese. Dependence on technology, lack of physical activity and consumption of extra caloric food than required are considered as causes of obesity. Obesity and NAFLD have increased significantly over the past decades. Although fatty liver is more common in obese people, sometimes thin people also suffer from fatty liver. Fatty liver disease can occur in certain types of drugs, alcohol, hormonal factors and hereditary factors. A BMI of 9 is overweight and a BMI of over 30 is considered overweight or obese. Dependence on technology, lack of physical activity and consumption of extra caloric food than required are considered as causes of obesity.
Obesity and NAFLD have increased significantly over the past decades. Although fatty liver is more common in obese people, sometimes thin people also suffer from fatty liver. Fatty liver disease can occur in certain types of drugs, alcohol, hormonal factors and hereditary factors. Sometimes thin people also suffer from fatty liver. Fatty liver disease can occur in certain types of drugs, alcohol, hormonal factors and hereditary factors. Sometimes thin people also suffer from fatty liver. Fatty liver disease can occur in certain types of drugs, alcohol, hormonal factors and hereditary factors.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or NAFLD can be divided into two types. One is normal fatty liver in which there is excess fat in the liver but no signs of liver inflammation or damage are seen on examination.
The other is non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis or NASH in which fatty liver inflammation or damage is diagnosed through physical symptoms and tests.
A study in our country found fatty liver in about 33 percent of people. In rural areas, the prevalence of this disease is higher among middle-aged women.
Continuity of signs, symptoms and disease
Fatty liver is a silent disease that usually produces no significant symptoms. However, fatigue or lethargy may be felt, sometimes a dull pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Patients with fatty liver who have diabetes are at increased risk of long-term liver disease. And those who suffer from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, develop symptoms of chronic liver inflammation. About 40 percent of patients with NASH may develop liver cirrhosis (shrinking of the liver and reduced blood flow).
However, even after liver cirrhosis, it can remain at a tolerable level for about 10 years. That is, at this time, the patient feels tired, lethargic, weak, but the liver continues its activities without any complications except for the decrease in performance.
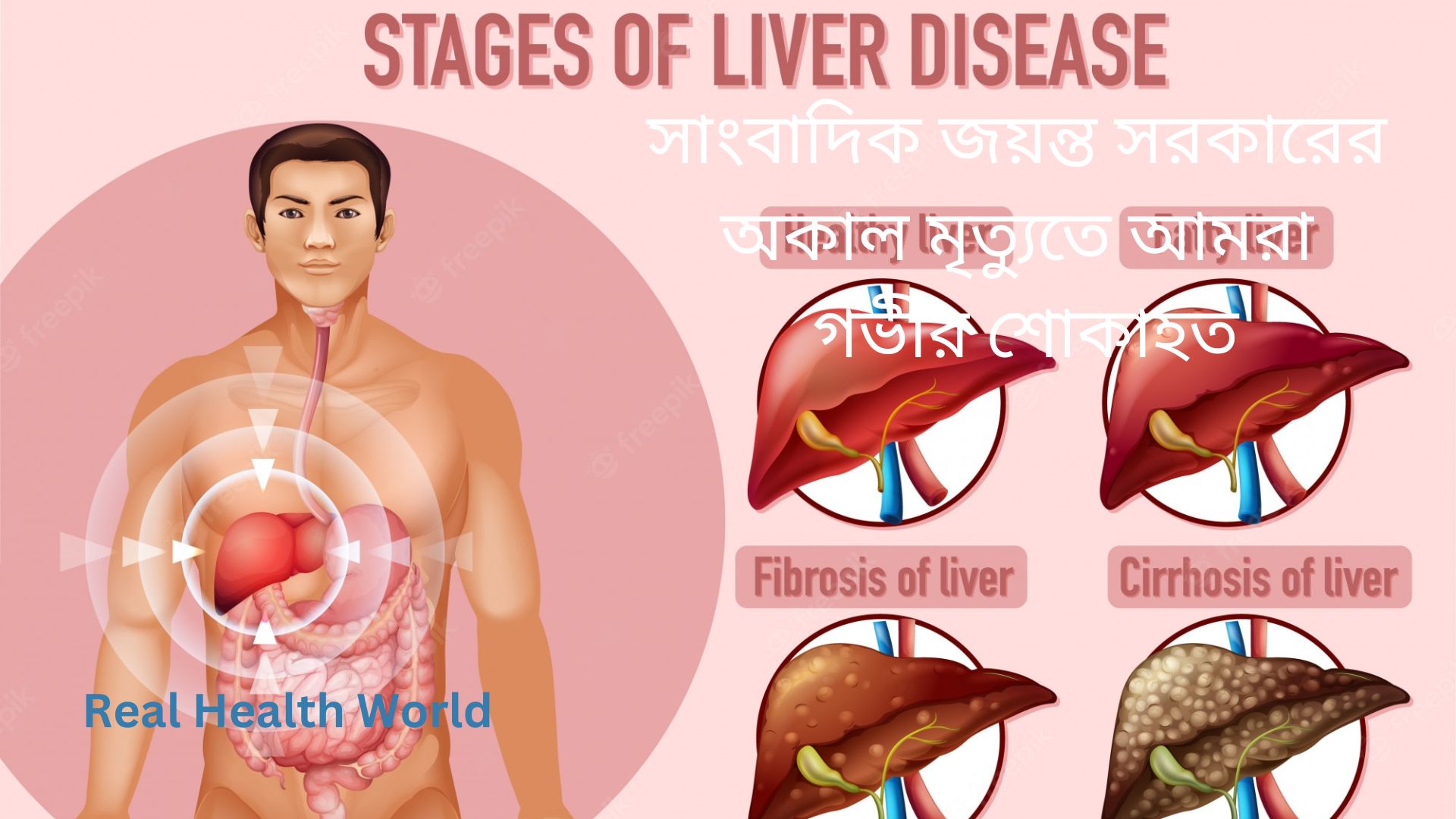
If this stage is exceeded, various complications of liver cirrhosis may occur, such as water in the stomach, legs, swelling of the vein in the esophagus and bleeding due to the rupture of the swollen vein, brain and kidney impairment. This condition is called Decompensated liver cirrhosis or the unbearable condition of liver cirrhosis. A significant number of patients with this condition are at risk of developing liver cancer. Patients with this stage of liver cirrhosis generally have a life expectancy of two years. Fatty liver is considered to be the leading cause of liver cirrhosis in the present world. However, some patients with fatty liver develop liver cirrhosis.
In most cases, you can stay healthy and normal through awareness after diagnosis.
Examination and diagnosis of diseases
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is usually diagnosed through abdominal ultrasonogram or other imaging tests such as CT scan, MRI etc.
Fatty liver is associated with insulin resistance. Insulin, which regulates blood sugar, also plays a role in the metabolism of various parts of the body. And in these patients, due to insulin resistance in the liver cells, the metabolic process cannot work properly, the amount of glucose and fat in the liver gradually increases. ‘Insulin resistance’ can be detected by measuring blood sugar and insulin levels.
Blood tests include liver enzymes such as SGPT, SGOT, bilirubin, albumin, blood lipids, blood sugar; Apart from this, hepatitis B, C infection should also be checked.
Note that diabetes, high blood pressure, excess blood fat, fatty liver risk with obesity also increases the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, cerebral venous disease, etc. An attempt should be made to detect these diseases through examination and to ensure the necessary advice and treatment.
Long-term liver inflammation gradually leads to the formation of scar tissue throughout the damaged liver, called liver fibrosis. In the later stages, numerous nodules form in this fibrous liver, a condition known as liver cirrhosis. The best way to detect liver inflammation, fibrosis and cirrhosis is through a liver biopsy where a special needle is used to examine tissue from the liver to measure liver damage. However, some non-invasive tests can measure liver fat and fibrosis without liver biopsy, one of which is FriboScan. Through this test, the condition of the liver can be understood before and after the treatment.
Treatment of Fatty Liver
There is no specific medicine for NAFLD or fatty liver. No medication can directly eliminate fatty liver. For this purpose, several drugs are already in various stages of research. However, although there are no approved drugs, several studies and trials have shown that certain drugs used in diabetes and other diseases and certain vitamins (such as ‘E’ vitamin) help reduce inflammation and fibrosis of fatty liver. So far, most emphasis has been placed on dietary changes and physical activity and exercise. Weight loss (at least 10 percent) is the first and foremost goal in treating fatty liver. In this case, changing the diet is very important. Carbohydrates like rice, bread, potatoes etc. should be eaten less. You can eat vegetables, fresh fruits in normal amount. Can eat enough fish (except oily part) but junk food, oily and fried food, meat, fatty food and cake-pastry,
Regular physical activity or exercise; Walking briskly for at least 30 minutes daily is an effective exercise for weight loss. In the western world, if needed, the stomach is shortened by bariatric surgery, it is not yet common in our country.
Diabetes, high blood pressure, blood cholesterol should be treated as advised by the doctor.
If liver cirrhosis and its complications occur due to fatty liver, at this stage the normal life of the patient can be reconfirmed by transplanting part of the liver from a healthy person into the patient’s body, in addition to general treatment.
A few liver transplants have already been done in our country. We are hopeful that liver transplantation will start in full swing in Bangladesh soon with the combination of government and private organizations. So awareness is important, not fear. By changing diet, losing weight through physical activity, taking regular medicines like doctor’s advice, patients with fatty liver can lead a healthy and normal life.
What are the 3 signs of a fatty liver?
- Abdominal swelling (ascites)
- Enlarged blood vessels just beneath the skin’s surface.
- Enlarged spleen.
- Red palms.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
How can I reduce a fatty liver?
- Lose weight. If you’re overweight or obese, reduce the number of calories you eat each day and increase your physical activity in order to lose weight. …
- Choose a healthy diet. …
- Exercise and be more active. …
- Control your diabetes. …
- Lower your cholesterol. …
- Protect your liver.
What is the root cause of fatty liver?
Eating excess calories causes fat to build up in the liver. When the liver does not process and break down fats as it normally should, too much fat will accumulate. People tend to develop fatty liver if they have certain other conditions, such as obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides.
Can fatty liver be cured completely?
The good news is that fatty liver disease can be reversed—and even cured—if patients take action, including a 10% sustained loss in body weight. “Dr. Fimmel’s diagnosis scared me,” admitted Molina.
What is the fastest way to cure a fatty liver?
Research suggests that losing weight is the single best thing you can do to control or reverse NAFLD. A good goal is to lose 10% of your total body weight, but even a loss of 3% to 5% can improve your liver health. Talk with your doctor about the best way for you to lose weight safely and effectively.
What foods should I avoid if I have a fatty liver?
6 types of foods to avoid if you have fatty liver disease
- Alcohol. Alcohol can be a major cause of fatty liver disease as well as other liver diseases.
- Added sugar. Stay away from sugary foods such as candy, cookies, sodas, and fruit juices. …
- Fried foods. …
- Added salt. …
- White bread, rice, and pasta. …
- Red meat.
What vitamins are good for liver repair?
Vitamins that play a crucial role in maintaining liver health include vitamin D, E, C, B. Individuals need to take these vitamins regularly through a healthy diet plan.
Read more from Real Health World